

At room temperature and pressure, it is in the solid state.
#RADIOACTIVE ELEMENT DEFINITION SERIES#
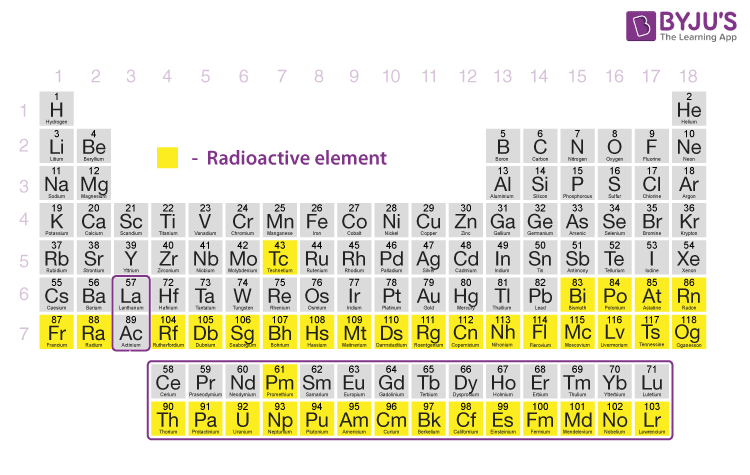
In the periodic table of elements, Plutonium can be found in the actinide series among f block elements. Plutonium is an artificial chemical element that has the atomic number 94 and symbol Pu. Key Terms: Plutonium (Pu), Radioactive Decay, Transuranium, Uranium (U) What is the Difference Between Plutonium and Uranium The main difference between Plutonium and Uranium is that Plutonium is highly radioactive whereas Uranium is weakly radioactive.

This property of undergoing radioactive decay causes Plutonium and Uranium to be used as components in explosives and energy sources. Uranium is also considered as a radioactive element because of its instability. Plutonium is a transuranium element that has the atomic number 94. All these transuranium elements are unstable and undergo radioactive decay. Table 1.Transuranium elements are chemical elements that have an atomic number greater than 92, the atomic number of Uranium element. The effective dating range of the carbon-14 method is between 100 and 50,000 years. For young organic materials, the carbon-14 (radiocarbon) method is used. For instance, geologists use the Sm-Nd (samarium-147/neodymium-143) method for determining the age of very old materials (e.g., meteorites and metamorphic rocks) or when a rock became crystallized (in the mantle) or metamorphosed (at a subduction zone). Depending on the half-life and the material being dated, various methods are used. Because decay occurs at a fixed rate (this is the key point), scientists can measure the amount of decayed material in the sample, determine the ratio between original and decayed material, and then calculate the sample’s age. When discussing decay rates, scientists refer to “half-lives”-the length of time it takes for one-half of the original atom of the radioactive isotope to decay into an atom of a new isotope. The rubidium-strontium method has been a popular method to determine the absolute age of geological processes. This results in a nucleus composed of 38 protons and 49 neutrons, corresponding to strontium’s nucleus of 87 atomic particles. By emitting a beta particle, the neutron is transformed into a proton. In addition the neutron emits a neutral particle that is called an antineutrino.
As explained on WebGeology from the University of Tormsø, Norway: One neutron of the nucleus emits a beta particle, which is identical to an electron. For instance, rubidium-87 (87Rb), an unstable element, becomes strontium-87 (87Sr), a stable element, via beta decay. This transformation happens via the emission of particles such as electrons (known as beta decay) and alpha particles. Radiometric decay occurs when the nucleus of a radioactive atom spontaneously transforms into an atomic nucleus of a different, more stable isotope. Geologists use these dates to further define the boundaries of the geologic periods shown on the geologic time scale. To determine the ages in years of Earth materials and the timing of geologic events such as exhumation and subduction, geologists utilize the process of radiometric decay. The term applies to all methods of age determination based on nuclear decay of naturally occurring radioactive isotopes.
#RADIOACTIVE ELEMENT DEFINITION PLUS#
Radiometric dating calculates an age in years for geologic materials by measuring the presence of a short-life radioactive element, e.g., carbon-14, or a long-life radioactive element plus its decay product, e.g., potassium-14/argon-40. Thermal ionization mass spectrometer used in radiometric dating.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
